JSON#
Join provides high-performance JSON serialization and deserialization built on the SAX API. The implementation supports standard JSON with optional extensions for comments and special numeric values.
JSON features:
- fast parsing — optimized number conversion and string handling
- pretty printing — configurable indentation
- canonical form — RFC 8785 compliant output
- flexible input — strings, streams, and file sources
- extended syntax — optional comments, Infinity, and NaN support
Serialization#
JsonWriter#
Serialize Value objects to JSON format:
#include <join/json.hpp>
using join;
Value data;
data["name"] = "Alice";
data["age"] = 30;
data["active"] = true;
std::ostringstream out;
JsonWriter writer(out);
writer.serialize(data);
std::cout << out.str() << "\n";
// {"name":"Alice","age":30,"active":true}
Pretty printing#
Enable indentation for readable output:
// Indent with 2 spaces per level
JsonWriter writer(out, 2);
writer.serialize(data);Output:
{
"name": "Alice",
"age": 30,
"active": true
}Special numeric values#
JsonWriter handles special IEEE 754 values:
Value data;
data.pushBack(std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity());
data.pushBack(-std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity());
data.pushBack(std::numeric_limits<double>::quiet_NaN());
JsonWriter writer(out);
writer.serialize(data);
// [Inf,-Inf,NaN]
Canonical JSON#
JsonCanonicalizer#
Produce RFC 8785 compliant canonical JSON:
Value data;
data["z_field"] = 1;
data["a_field"] = 2;
data["m_field"] = 3;
std::ostringstream out;
JsonCanonicalizer canonicalizer(out);
canonicalizer.serialize(data);
// {"a_field":2,"m_field":3,"z_field":1}
Canonical JSON features:
- Sorted keys — object members ordered lexicographically by UTF-16 code units
- No whitespace — compact output without spaces or newlines
- Normalized numbers — integers without decimal points, consistent exponent format
- Special values as null — Infinity and NaN converted to
null
Deserialization#
JsonReader#
Parse JSON from various sources:
Value root;
JsonReader reader(root);
// From string
if (reader.deserialize(jsonString) == 0)
{
std::cout << root["name"].getString() << "\n";
}Input sources#
JsonReader accepts multiple input types:
// C-string with length
reader.deserialize(cstr, length);
// Pointer range
reader.deserialize(first, last);
// std::string
reader.deserialize(str);
// String stream
std::stringstream ss(jsonData);
reader.deserialize(ss);
// File stream
std::ifstream file("data.json");
reader.deserialize(file);
// Generic input stream
std::istream& stream = ...;
reader.deserialize(stream);Parse modes#
Control parsing behavior with JsonReadMode flags:
ParseComments#
Enable C-style comment parsing:
std::string json = R"({
// Single-line comment
"name": "Alice",
/* Multi-line
comment */
"age": 30
})";
Value root;
JsonReader reader(root);
reader.deserialize<JsonReadMode::ParseComments>(json);ValidateEncoding#
Enforce strict UTF-8 validation (currently not implemented).
StopParsingOnDone#
Stop parsing after first complete value, allowing trailing data:
std::string json = R"({"a":1}{"b":2})";
Value root;
JsonReader reader(root);
reader.deserialize<JsonReadMode::StopParsingOnDone>(json);
// root contains {"a":1}, trailing {"b":2} ignored
Combining modes#
Use bitwise OR to combine flags:
reader.deserialize<JsonReadMode::ParseComments | JsonReadMode::StopParsingOnDone>(json);Extended numeric syntax#
JsonReader supports extended number formats:
std::string json = R"([Infinity, -Infinity, NaN, -NaN])";
Value root;
JsonReader reader(root);
reader.deserialize(json);
// root[0] → +∞
// root[1] → -∞
// root[2] → NaN
// root[3] → -NaN
Supported formats:
Infinity,Inf(case insensitive)-Infinity,-InfNaN(case insensitive)-NaN
Error handling#
JSON error codes#
| Error Code | Description |
|---|---|
InvalidComment | Malformed comment syntax |
InvalidEscaping | Invalid escape sequence in string |
InvalidEncoding | Invalid UTF-8 or Unicode encoding |
IllegalCharacter | Illegal control character |
MissingCurlyBracket | Missing } in object |
MissingSquareBracket | Missing ] in array |
MissingQuote | Missing " in string |
MissingColon | Missing : after object key |
MissingComma | Missing , between elements |
EndOfFile | Unexpected end of input |
Checking errors#
if (reader.deserialize(json) == -1)
{
if (lastError == JsonErrc::InvalidEscaping)
{
std::cerr << "Bad escape sequence\n";
}
else
{
std::cerr << "Parse error: " << lastError.message() << "\n";
}
}Performance characteristics#
Streaming parser#
JsonReader uses on-the-fly parsing to minimize memory usage:
- No intermediate buffering — processes input directly from source
- Constant memory overhead — memory usage independent of input size
- Stream-friendly — works efficiently with file streams and network sockets
Fast path number parsing#
JsonReader uses optimized algorithms:
- Fast integer conversion — direct computation for integers up to 19 digits
- Fast double conversion — custom floating-point parser for common cases
- Fallback to strtod — standard library for edge cases
String handling#
- Batch copying — continuous unescaped sequences copied efficiently
- Escape lookup table — O(1) escape character detection
- UTF-8 passthrough — no validation overhead by default
Benchmark results#
Join has been benchmarked against other JSON libraries using nativejson-benchmark:
Conformance#
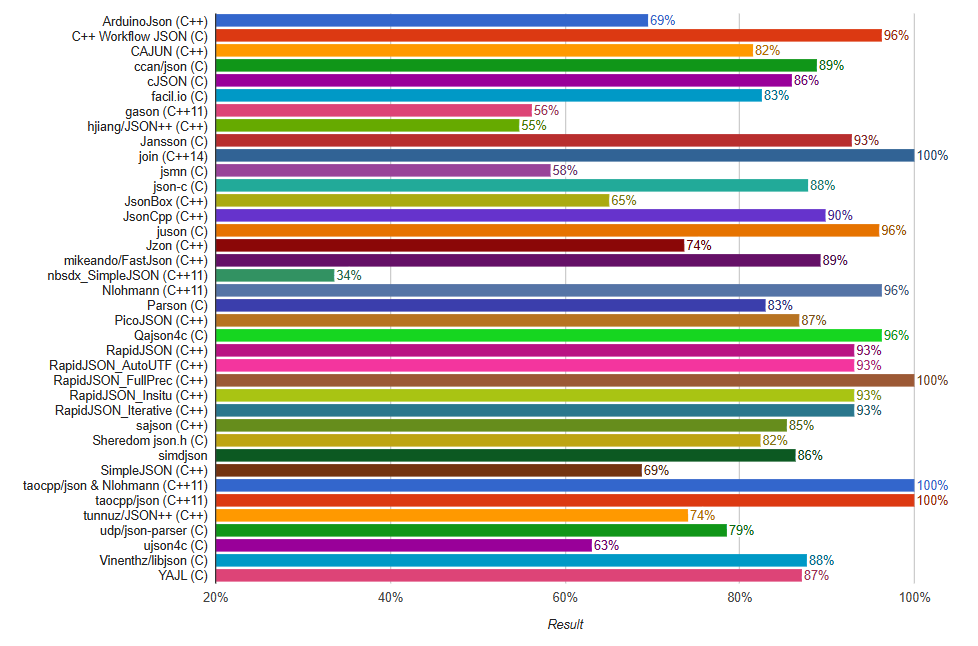
Join achieves 100% conformance on the standard JSON test suite, matching the top-performing libraries.
Parse performance#
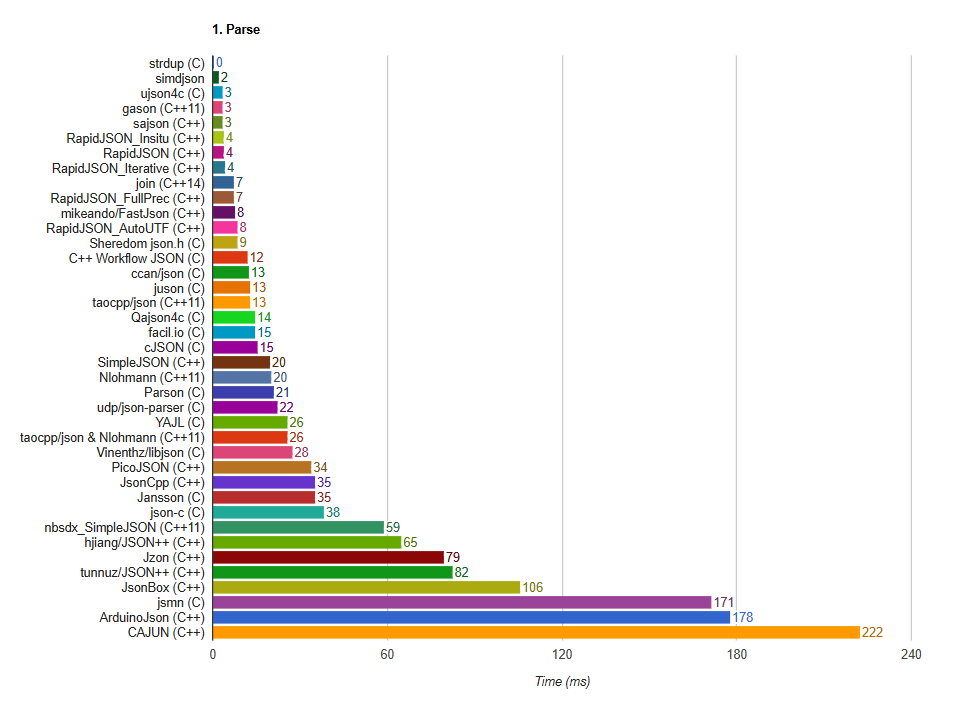
Join delivers competitive parsing speed, ranking among the fastest C++ JSON parsers while maintaining full standard compliance.
Best practices#
- Use canonical form for deterministic output (signing, hashing, comparison)
- Enable indentation for human-readable files, disable for network protocols
- Check return values — all operations return
-1on error - Parse comments only when needed — adds parsing overhead
- Reuse reader/writer objects — avoid repeated construction
- Stream large files — use file streams instead of loading into memory
Example usage#
Complete round-trip#
#include <join/json.hpp>
#include <join/value.hpp>
using join;
// Create data
Value data = Object{
{"users", Array{
Object{{"name", "Alice"}, {"id", 1}},
Object{{"name", "Bob"}, {"id", 2}}
}},
{"count", 2}
};
// Serialize to JSON
std::ostringstream out;
JsonWriter writer(out, 2); // 2-space indentation
writer.serialize(data);
std::string json = out.str();
std::cout << json << "\n";
// Parse back
Value parsed;
JsonReader reader(parsed);
if (reader.deserialize(json) == 0)
{
std::cout << "User count: " << parsed["count"].getInt() << "\n";
std::cout << "First user: " << parsed["users"][0]["name"].getString() << "\n";
}Summary#
| Feature | Supported |
|---|---|
| Standard JSON parsing | ✅ |
| Pretty printing | ✅ |
| Canonical JSON (RFC 8785) | ✅ |
| Comment parsing | ✅ |
| Extended numerics | ✅ |
| Multiple input sources | ✅ |
| Optimized performance | ✅ |
| Unicode escape sequences | ✅ |